Table of Contents
🧬 Improving Protein Docking Accuracy with Iter-CONSRANK
Increasing the Fraction of Correct Solutions in Ensembles of Protein-Protein Docking Models by an Iterative Consensus Algorithm
KVL Staff on Project
Didier Barradas Bautista
didier.barradasbautista@kaust.edu.sa
Building 1, Level 0, Office 0125
![]() KAUST PI on Project
KAUST PI on Project
Luigi Cavallo
luigi.cavallo@kaust.edu.sa
Research Breakthrough
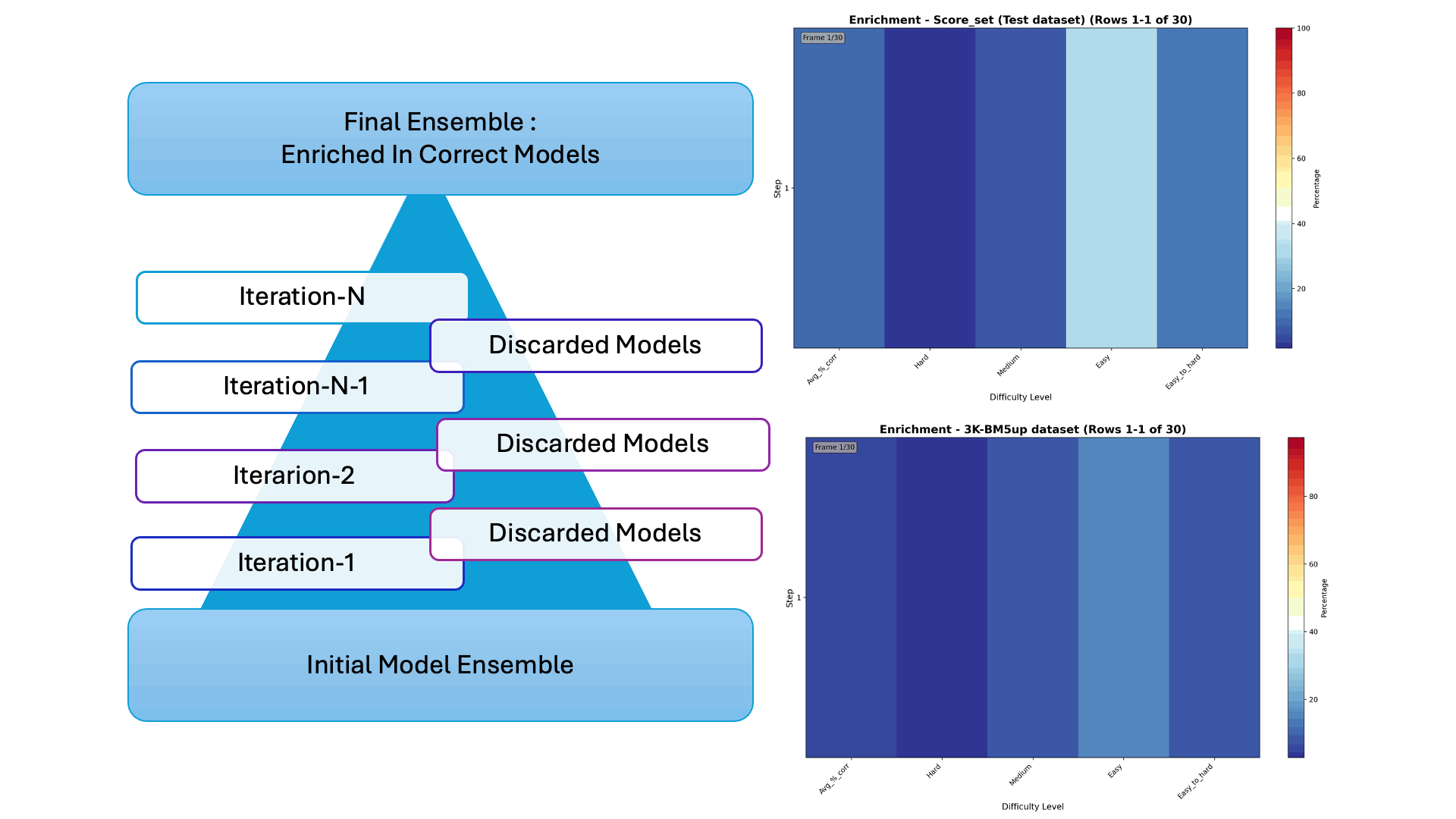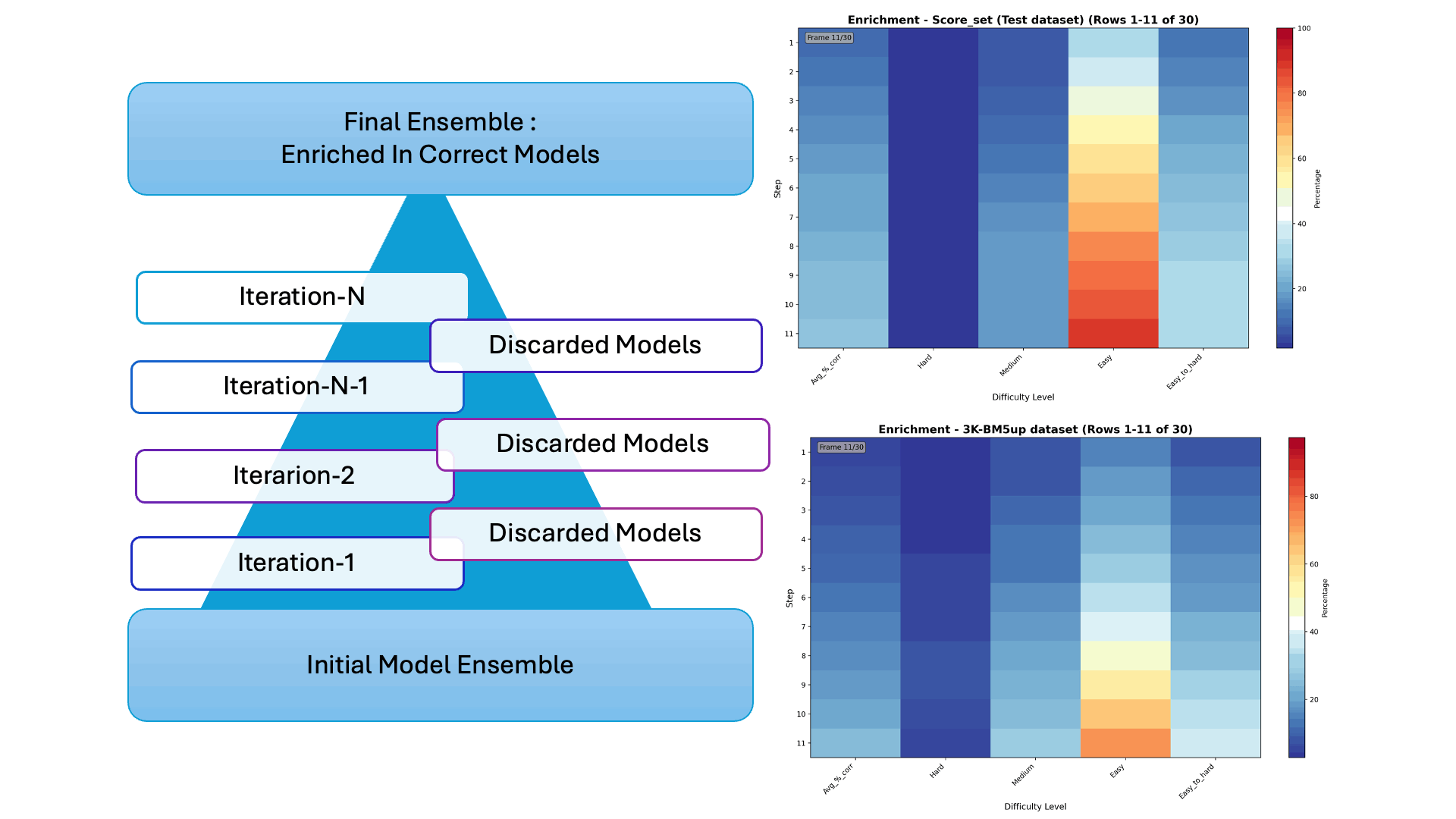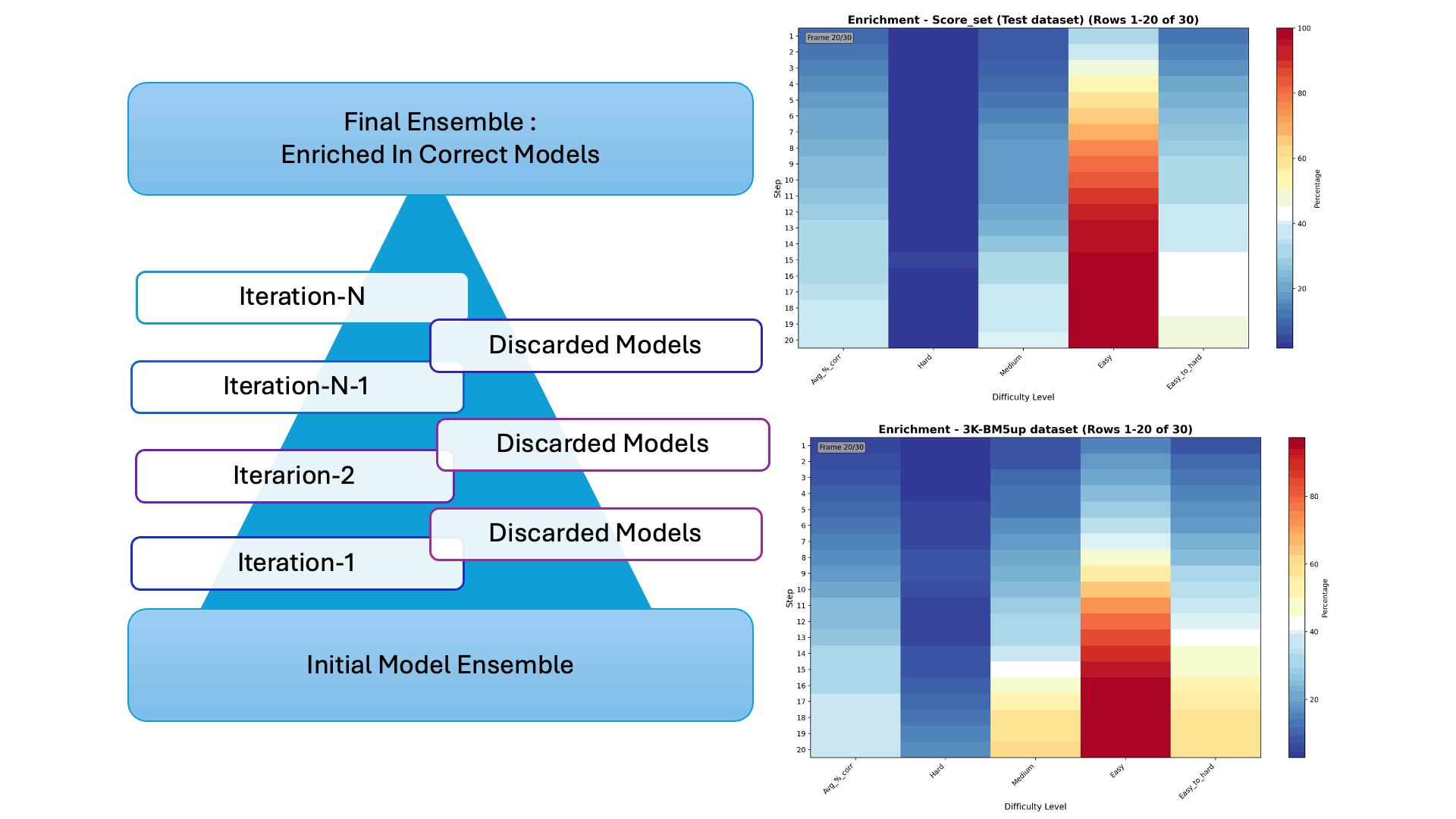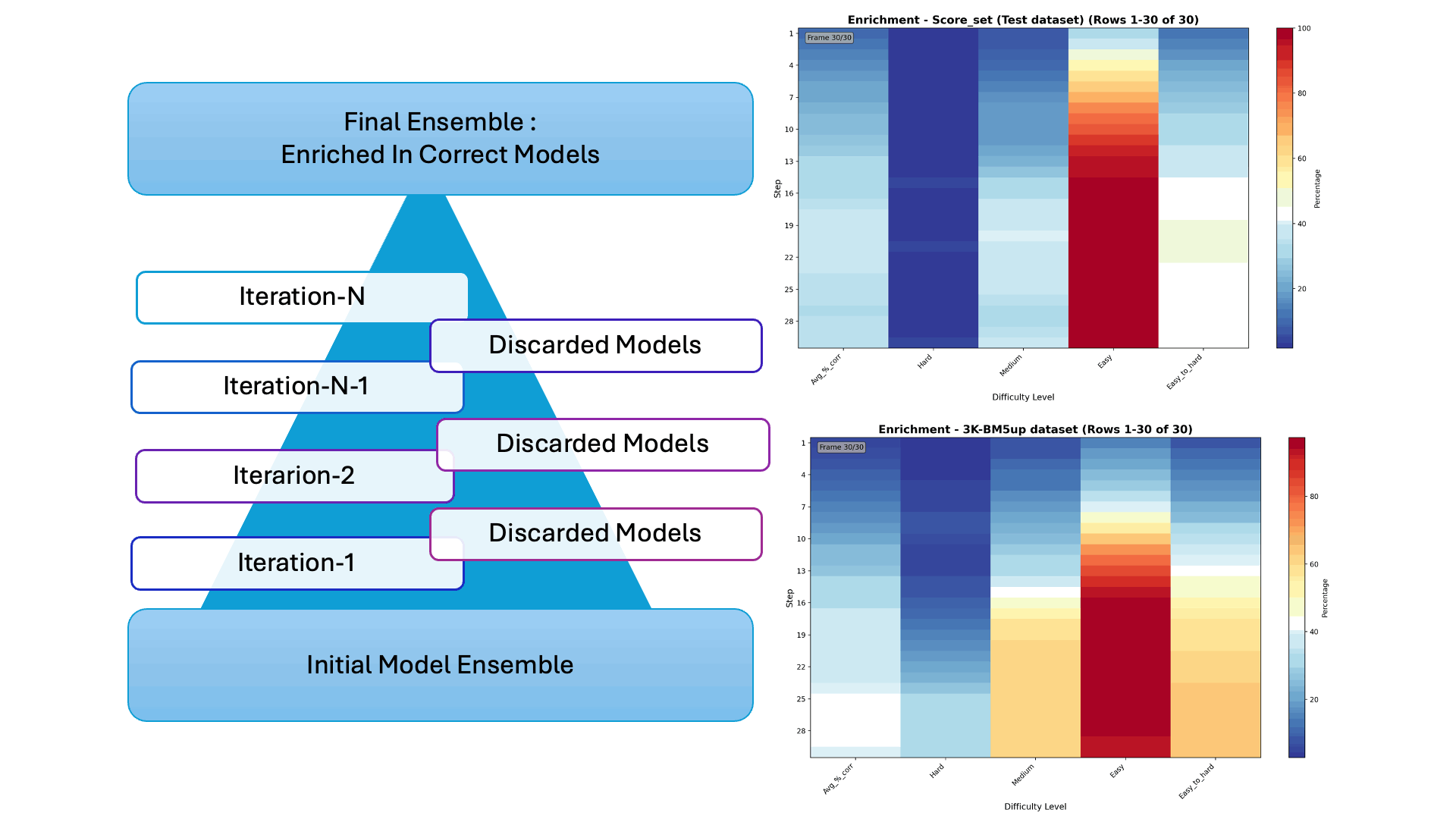
Protein–protein docking generates thousands of possible interaction models—but only a few are correct. In our latest collaborative work, we introduce Iter-CONSRANK, an iterative scoring algorithm that filters out incorrect models and enriches the ensemble with correct ones.
- 📊 Tested on two challenging datasets, Iter-CONSRANK increased the fraction of correct models by up to 8× for medium-difficulty targets and outperformed over 150 scoring functions in ranking accuracy.
- 🎯 The method is available for use in pre-processing docking ensembles or as an independent scoring tool.
- 🔬 This work was led in collaboration with Luigi Cavallo and our partners at the University of Naples “Parthenope”
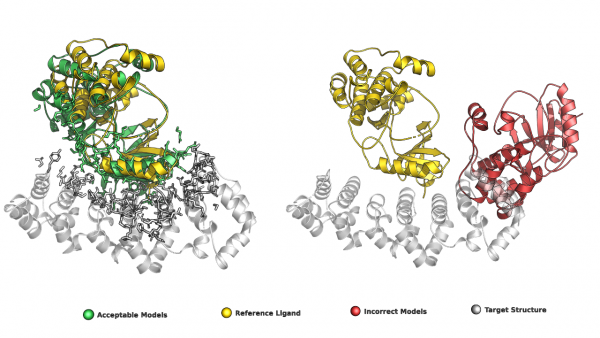
🔬 Research Visualization The graphical abstract below illustrates the iterative filtering strategy used to enrich correct protein–protein docking models. The paper entitled “Increasing the Fraction of Correct Solutions in Ensembles of Protein-Protein Docking Models by an Iterative Consensus Algorithm” is available for download and review. here.
🎯 KVL's Contribution: KVL's visualization scientist Didier Barradas-Bautista contributed significantly to the development and validation of the Iter-CONSRANK algorithm through:
- Design and implementation of contact-based clustering to enhance scoring accuracy
- Generation of the 3K-BM5up benchmark dataset using multiple docking tools
- Optimization of iteration parameters and performance evaluation across difficulty categories
- Comparative benchmarking against 157 scoring functions, demonstrating top performance
- Public release of the Iter-CONSRANK software for community use
- Active participation in CAPRI scoring rounds, validating the method in blind tests